Methanol, as both a chemical building block and a fuel, can support the transition to a low-carbon economy.
Methanol can help meet the increased demand for petrochemicals-based products and reduce air pollution and GHG emissions from combustion-related applications. Methanol can also be made from renewable sources, supporting the long-term decarbonization of both the chemicals that make modern life possible and the transportation sector. By leveraging our existing production assets and leading market position and by collaborating with government and industry, we will drive solutions that can meet growing demand for our product in ways that respect the environmental commitments of our company, industry and customers.
Methanex’s Priorities
Three priorities guide our approach to the transition to a low-carbon economy: reducing emissions from manufacturing, producing lower-carbon methanol, and growing markets for methanol. 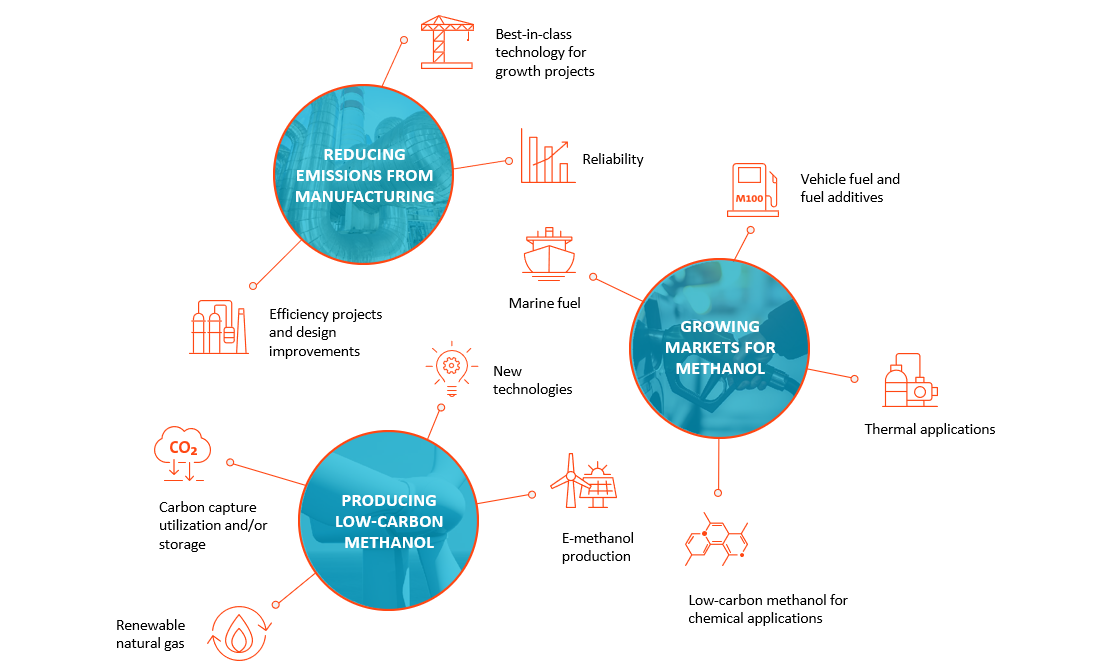
Reducing Emissions from Conventional Methanol
Methanex is taking concrete steps to achieve our 10% GHG intensity reduction target by 2030, exploring multiple pathways to reduce the carbon intensity of our existing methanol plants. We continue to focus on plant efficiency, plant reliability and the use of catalysts at all our plants and are identifying ways to upgrade our existing facilities to improve energy efficiency and lower GHG emissions. These efforts have already resulted in a five per cent decrease in emissions intensity since 2019. We also carried out a preliminary assessment of our Scope 3 GHG emissions in 2023, which has identified key sources of emissions as natural gas and third-party purchased methanol.
Efficiency Projects and Design Improvements
|
We invested more than $15 million into projects with GHG reduction benefits that will help us avoid 60,000 tonnes of CO2e per year. |
Best-in-class Technology for Growth
|
G3 is expected to have one of the lowest CO₂ emissions intensity profiles in the industry, with Scope 1 and 2 emission less than 0.3 tonnes of CO₂ per tonne of methanol. |
Reliability
|
We had strong global plant reliability of 95.9% in 2023. To maintain high reliability, we focus on preventive maintenance, condition monitoring for critical assets, and risk-based inspection for static equipment. |
In 2024, we will carry out work to quantify these sources. To read more about how we are working to reduce emissions from conventional production across our sites and about our 20+ efficiency projects in place, please see pages 24 to 26 of the 2023 Sustainability Report.
Producing Lower-Carbon Methanol
Carbon Capture Utilization and/or Storage
Conventional methanol production coupled with carbon capture and storage (CCS) produces what is known as blue methanol. CCS is the process of capturing CO₂ from fuel combustion or industrial processes, purifying and compressing the CO₂, and transporting it via pipeline to be stored underground in deep geological formations. Some industrial processes, such as the production of methanol, also have the option to reuse the captured CO₂ as feedstock, known as carbon capture, utilization and storage Methanex has confirmed the technical feasibility of CCUS at our Medicine Hat and Geismar sites—the most promising locations for implementing this technology. Despite technical feasibility, project economics require a price premium for blue methanol and we continue to gauge customer interest. 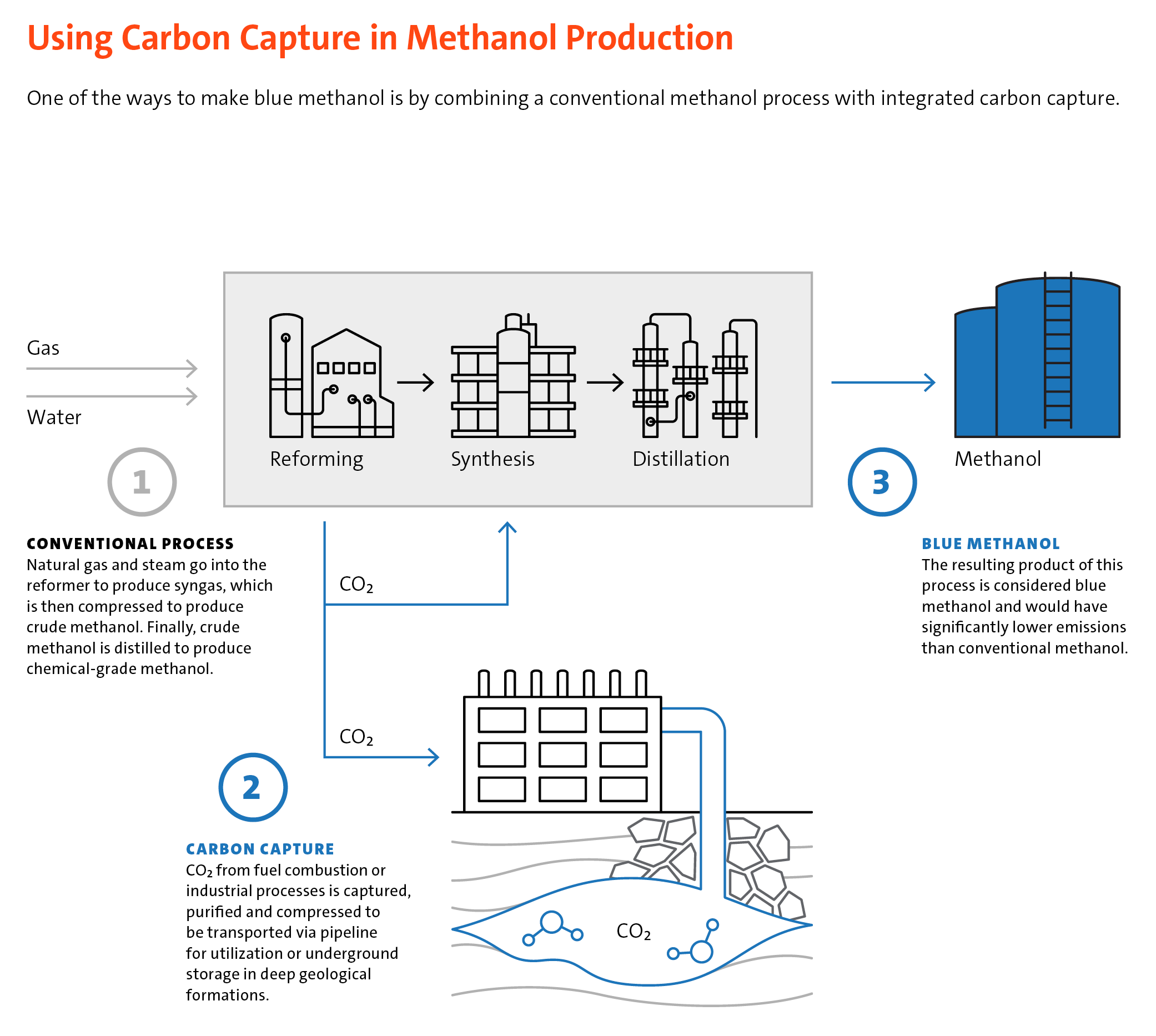 Note: This diagram is for illustrative purposes only and represents how carbon capture could potentially be applied at a steam-reforming methanol plant. To read more about Carbon Capture Utilization and/or Storage please visit page 28 of the 2023 Sustainability Report.
Note: This diagram is for illustrative purposes only and represents how carbon capture could potentially be applied at a steam-reforming methanol plant. To read more about Carbon Capture Utilization and/or Storage please visit page 28 of the 2023 Sustainability Report.
Renewable Natural Gas
Using renewable natural gas or biomass in a conventional methanol process results in a form of green methanol called bio-methanol. Our Geismar, U.S. site and our Dallas and Brussels offices have been certified with the International Sustainability & Carbon Certification (ISCC) to produce and sell biomethanol since 2020. The ISCC process certifies the origin of the product and the chain of custody to support traceability and transparency in supply chains. This certification enables sales of biomethanol to chemical customers in Europe enabling them to produce low-carbon products like bio-based polymers. While renewable natural gas costs significantly more than conventional natural gas feedstock, making biomethanol more expensive to produce, this process requires no incremental improvements or capital investments to our manufacturing facilities.
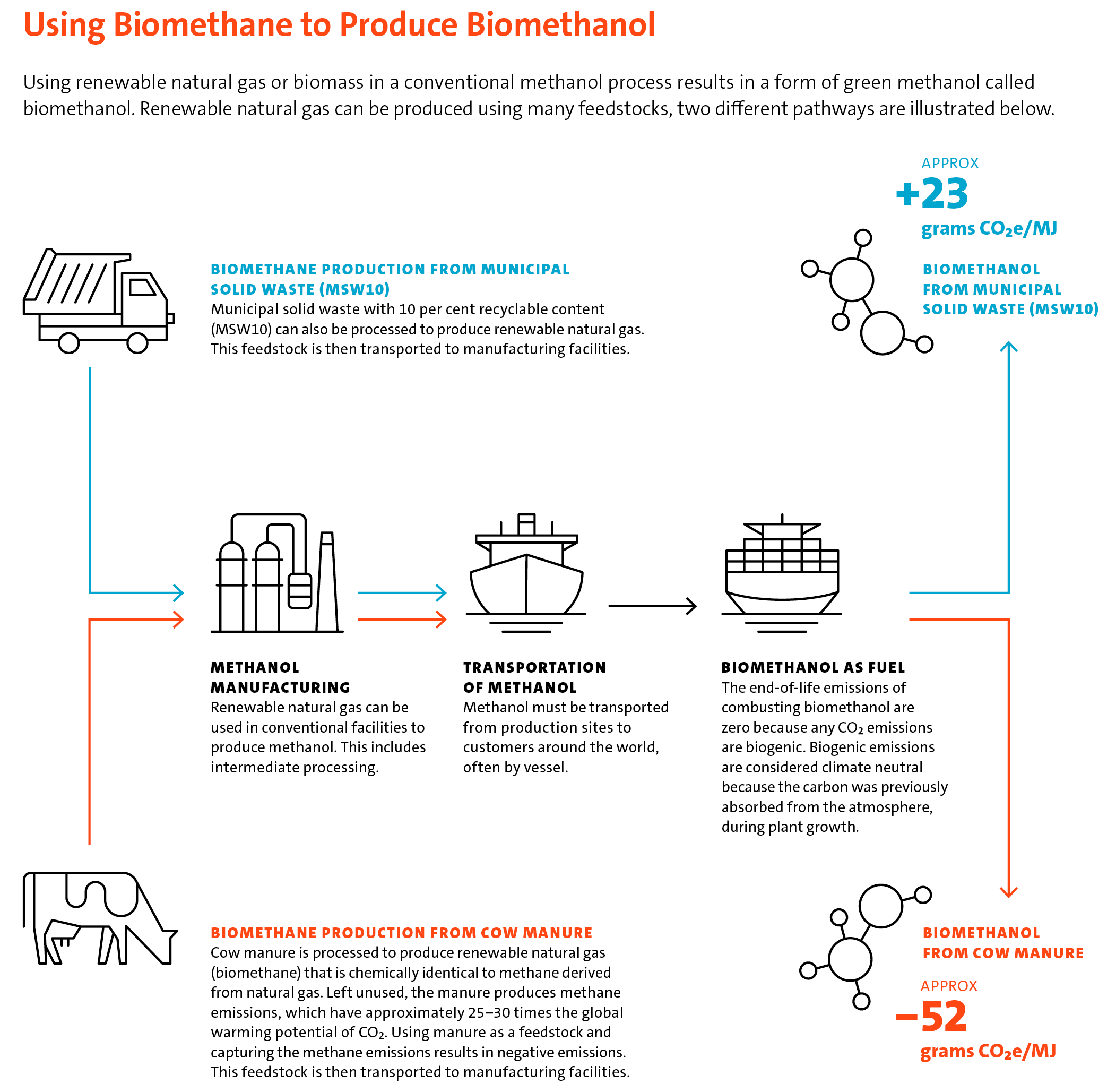
Our Geismar plant remains positioned to respond to customer using renewable natural gas. To read more about Renewable Natural Gas visit page 29 of the 2023 Sustainability Report.
E-methanol Production
There are several ways to produce e-methanol. Methanex is exploring pathways to gradually decarbonize our existing plants, including opportunities to use renewable electricity to produce green hydrogen and combine this with industrial or biogenic CO₂ from third parties to produce e-methanol. In 2023, we conducted a technical and economic feasibility study of incorporating electrolyzers (to produce hydrogen from renewable power) at our existing plants. The study focused on evaluating technologies and critical requirements for the economic viability of producing e-methanol, rather than the feasibility at a particular site. In 2024, we plan to further explore the feasibility of e-methanol specifically at our Geismar, U.S. and Damietta, Egypt sites.
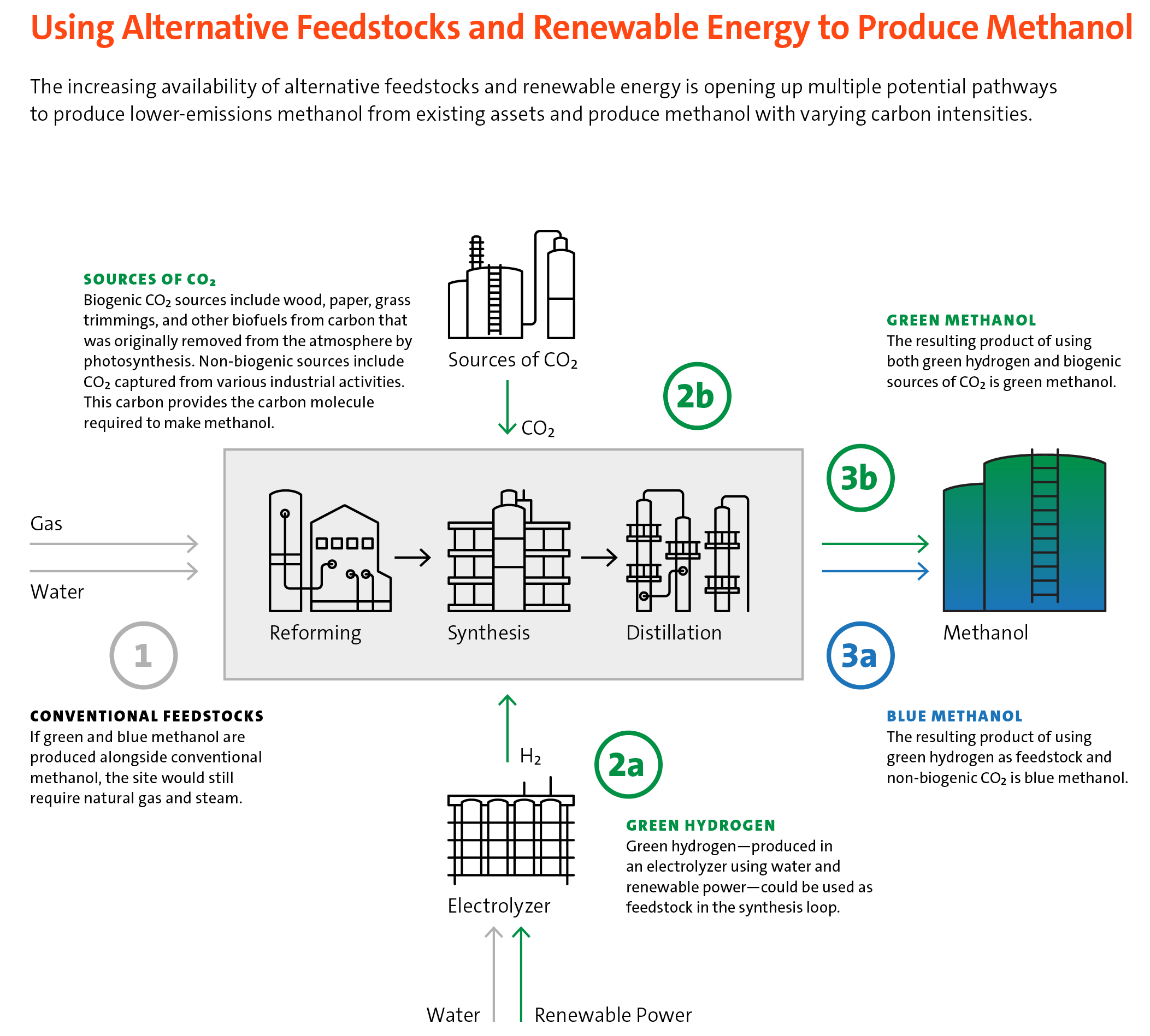 Note: This diagram is for illustrative purposes only and represents how alternative feedstocks and renewable energy could be applied at a steam-reforming methanol plant. To read more about E-methanol and Using Alternative Feedstocks and Renewable Energy to Produce Methanol please visit page 30 of the 2023 Sustainability Report.
Note: This diagram is for illustrative purposes only and represents how alternative feedstocks and renewable energy could be applied at a steam-reforming methanol plant. To read more about E-methanol and Using Alternative Feedstocks and Renewable Energy to Produce Methanol please visit page 30 of the 2023 Sustainability Report.
Growing Markets for Methanol
Methanex is committed to growing markets for methanol as a chemical feedstock and fuel. We continue to promote the emissions benefits of methanol and leverage our investments and existing assets to develop a market for conventional and low-carbon methanol as a “futureproof” fuel for a low-carbon economy. Methanol can be produced using many different feedstocks and methods but the resulting product is chemically identical.
Marine Fuel
|
The market for methanol as a marine fuel is a significant opportunity for Methanex. With maritime fuel regulations focused on lowering the GHG emissions of marine fuels, shipping companies actively pursuing decarbonization pathways, and governments negotiating green corridors with the goal to accelerate the decarbonization of the maritime shipping industry, the demand for fuels with decarbonization pathways is expected to continue to grow. There are 20 green corridors (a route that links ports offering low-carbon or zero-emissions fuels or solutions) globally under discussion today. 2023 was the first year that orders for dual-fuel methanol ships outpaced LNG-powered ships; based on the current order book by the end of 2028 there will be over 250 methanol ships on the water. Waterfront Shipping who pioneered the methanol engine has 19 dual-fuel methanol ships. Biomethanol and e-methanol are two of the few fuels that can qualify as a green fuel under EU regulations. We are working to develop low-carbon methanol supply to meet the growing demand. In 2023, we joined the Maersk Mc-Kinney Moller Center for Zero Carbon Shipping as a Mission Ambassador, which is a collaborative effort across the value chain to drive sustainable decarbonization of the maritime industry by 2050. To read more about Methanol as a Marine fuel visit here or learn more on pages 32 to 35 of the 2023 Sustainability Report. |
Methanol as a Cleaner-Burning Vehicle Fuel
|
Methanol is an affordable substitute for gasoline and diesel in countries looking to transition away from fuels that contribute to high levels of air pollution. Methanol’s efficient combustion, safety, ease of distribution and wide availability around the world make it an attractive alternative fuel for transportation. Methanol can be used as a transportation fuel in four ways:
To read more about methanol as a vehicle fuel, please see the Vehicle Fuel & Thermal Applications page of the website and pg. 36 of the 2023 Sustainability Report. |
Chemical Applications
|
We sell low-carbon methanol from our ISCC certified Geismar site into traditional chemical applications in Europe today and are talking with other chemical customers about how we can support their decarbonization goals. |
Other Applications for Methanol as a Cleaner-Burning Fuel
To read about how methanol can be used as a fuel for thermal applications, such as industrial boilers kilns, heating furnaces, as well as a cooking fuel, please see the Vehicle Fuel & Thermal Applications page of the website and page 37 of the 2023 Sustainability Report.